The Principle of NTC Temperature Sensors
Have you ever used a temperature sensor? Do you know how temperature sensors work? Now let’s discuss the principle of temperature sensors
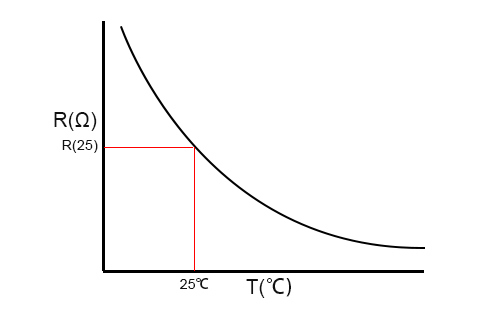
NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) temperature sensors are vital components used in various electronic devices and systems to measure temperature accurately. The principle behind NTC temperature sensors lies in their electrical resistance, which decreases as temperature rises.
The NTC temperature sensor is composed of a special element called an NTC thermistor, which is a resistance element that can change the resistance value according to temperature changes. NTC thermistors are made of conductive ceramics or thermoplastic plastics and have a strong electric heating effect. As the temperature increases, the resistance value of NTC thermistor will also increase, and as the temperature decreases, its resistance value will also decrease. Therefore, NTC thermistors can convert temperature changes into resistance value changes, thereby obtaining temperature information.
At the heart of an NTC temperature sensor is a thermistor, typically made of a semiconductor material such as ceramic or polymer. As temperature changes, the conductivity of the semiconductor material changes accordingly, resulting in a corresponding change in resistance.
This unique characteristic allows NTC temperature sensors to provide precise temperature measurements across a wide range of applications, from automotive engines and home appliances to medical devices and industrial processes.
By harnessing the principle of NTC temperature sensors, engineers and designers can develop innovative solutions that enhance efficiency, reliability, and safety in various industries, ultimately improving the quality of our daily lives.