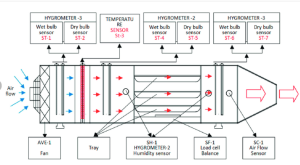
Abstract
Temperature sensors have revolutionized the field of drying technology, playing a pivotal role in ensuring efficient and safe drying processes. This article comprehensively explores the fundamental principles of temperature sensors, their integration and applications in various types of dryers, the associated advantages, and a glimpse into the potential future developments in this domain.
Introduction
Temperature sensors are devices designed to measure temperature in a precise and accurate manner. Their applications span across various industries, and in recent years, they have significantly impacted the field of drying technology. This article delves into the principles, applications, and future prospects of temperature sensors in dryers, encompassing a broad range of topics to provide a comprehensive understanding of their significance.
Part 1: Fundamental Principles of Temperature Sensors
Understanding the core principles of temperature sensors is essential for comprehending their application in drying technology. There are several types of temperature sensors, including thermocouples, RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors), thermistors, and infrared sensors. Each type operates on distinct principles and has unique advantages and disadvantages.
1.1 Thermocouples
Thermocouples are temperature sensors made of two different conductive metals joined at one end. When this end is exposed to a temperature gradient, it generates a voltage that is proportional to the temperature difference, enabling accurate temperature measurements.
1.2 RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors)
RTDs function based on the principle that the electrical resistance of certain materials changes with temperature. The resistance of the RTD element increases with rising temperature in a precise and predictable manner, allowing for accurate temperature measurements.
1.3 Thermistors
Thermistors are temperature-sensitive resistors made from ceramic materials. They exhibit a significant change in resistance with temperature, making them ideal for temperature sensing applications.
1.4 Infrared Sensors
Infrared sensors measure temperature by detecting the emitted infrared radiation from an object. They are non-contact sensors and are particularly useful for measuring the temperature of moving objects or in applications where contact sensors may not be suitable.
Part 2: The Role of Temperature Sensors in Various Dryer Types
Temperature sensors play a critical role in multiple types of dryers, optimizing the drying process by ensuring precise temperature control and safety.
2.1 Convection Dryers
In convection dryers, temperature sensors are strategically placed to monitor and regulate the hot air that circulates within the drying chamber. These sensors enable precise control over the drying temperature, ensuring optimal drying conditions for various materials and loads.
2.2 Drum Dryers
Drum dryers, commonly used in laundry applications, utilize temperature sensors to regulate the heat applied to the drum. These sensors ensure that the drum remains within the desired temperature range, effectively drying the laundry without causing damage.
2.3 Spray Dryers
Spray dryers employ temperature sensors to monitor and control the temperature of the drying gas or air. This control is crucial for achieving the desired particle size and moisture content in the final product.
2.4 Microwave Dryers
Microwave dryers, a modern innovation, utilize temperature sensors to precisely control microwave power, ensuring that the material being dried is exposed to the right amount of heat. These sensors help in avoiding over-drying or overheating.
Part 3: Advantages of Temperature Sensors in Drying Technology
Temperature sensors offer a plethora of advantages when incorporated into drying processes, enhancing efficiency, safety, and overall performance.
3.1 Enhanced Efficiency
Temperature sensors enable precise temperature control, optimizing the drying process for maximum efficiency. They facilitate faster drying times and reduce energy consumption, making the drying process more economical.
3.2 Improved Product Quality
With accurate temperature monitoring and control, temperature sensors aid in preserving the quality of the dried product. They prevent over-drying, ensuring that the final product retains its intended properties and characteristics.
3.3 Energy Efficiency
By ensuring that the drying process operates at the most suitable temperature, temperature sensors contribute to significant energy savings. This is particularly important in today’s world, where energy conservation is a key concern.
Part 4: Future Prospects and Advancements
Temperature sensors continue to evolve, and advancements in technology pave the way for innovative applications and enhanced capabilities.
4.1 Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Incorporating temperature sensors into drying processes, along with AI and machine learning algorithms, will enable predictive and adaptive temperature control. The system can learn from previous drying cycles and make real-time adjustments for the most efficient drying outcome.
4.2 IoT-Enabled Smart Dryers
The integration of temperature sensors with the Internet of Things (IoT) will facilitate smart drying systems. Users will have the ability to remotely monitor and control their dryers through mobile applications, optimizing drying cycles based on preferences and requirements.
4.3 Sustainable Sensor Technology
In the pursuit of sustainability, there is a growing focus on developing temperature sensors using eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes. Sustainable temperature sensors will not only reduce the environmental footprint but also contribute to a greener future.
Conclusion
Temperature sensors have emerged as indispensable components in modern drying technology. Their precise temperature measurement and control capabilities are crucial for efficient drying processes, ultimately leading to energy savings and enhanced product quality. As technology advances, the integration of temperature sensors with AI, IoT, and sustainable materials will drive the future of drying technology, making it more efficient, eco-friendly, and user-centric. The potential applications and benefits of temperature sensors in drying technology are vast, promising a bright future for this evolving field.